The QLCDNumber widget displays a number with LCD-like digits. More...
#include <QLCDNumber>
Inherits: QFrame.
| enum | Mode { Hex, Dec, Oct, Bin } |
| enum | SegmentStyle { Outline, Filled, Flat } |
|
|
| QLCDNumber ( QWidget * parent = 0 ) | |
| QLCDNumber ( uint numDigits, QWidget * parent = 0 ) | |
| ~QLCDNumber () | |
| bool | checkOverflow ( double num ) const |
| bool | checkOverflow ( int num ) const |
| int | digitCount () const |
| int | intValue () const |
| Mode | mode () const |
| SegmentStyle | segmentStyle () const |
| void | setDigitCount ( int numDigits ) |
| void | setMode ( Mode ) |
| void | setSegmentStyle ( SegmentStyle ) |
| bool | smallDecimalPoint () const |
| double | value () const |
| virtual QSize | sizeHint () const |
| void | display ( const QString & s ) |
| void | display ( double num ) |
| void | display ( int num ) |
| void | setBinMode () |
| void | setDecMode () |
| void | setHexMode () |
| void | setOctMode () |
| void | setSmallDecimalPoint ( bool ) |
| void | overflow () |
| virtual bool | event ( QEvent * e ) |
| virtual void | paintEvent ( QPaintEvent * ) |
The QLCDNumber widget displays a number with LCD-like digits.
It can display a number in just about any size. It can display decimal, hexadecimal, octal or binary numbers. It is easy to connect to data sources using the display() slot, which is overloaded to take any of five argument types.
There are also slots to change the base with setMode() and the decimal point with setSmallDecimalPoint().
QLCDNumber emits the overflow() signal when it is asked to display something beyond its range. The range is set by setDigitCount(), but setSmallDecimalPoint() also influences it. If the display is set to hexadecimal, octal or binary, the integer equivalent of the value is displayed.
These digits and other symbols can be shown: 0/O, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5/S, 6, 7, 8, 9/g, minus, decimal point, A, B, C, D, E, F, h, H, L, o, P, r, u, U, Y, colon, degree sign (which is specified as single quote in the string) and space. QLCDNumber substitutes spaces for illegal characters.
It is not possible to retrieve the contents of a QLCDNumber object, although you can retrieve the numeric value with value(). If you really need the text, we recommend that you connect the signals that feed the display() slot to another slot as well and store the value there.
Incidentally, QLCDNumber is the very oldest part of Qt, tracing its roots back to a BASIC program on the Sinclair Spectrum.
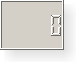 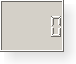   |
| LCD number widgets shown in various widget styles (from left to right): Motif, CDE, Windows, Windows XP, Macintosh, Plastique. |
See also QLabel, QFrame, Digital Clock Example, and Tetrix Example.
This type determines how numbers are shown.
| Constant | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| QLCDNumber::Hex | 0 | Hexadecimal |
| QLCDNumber::Dec | 1 | Decimal |
| QLCDNumber::Oct | 2 | Octal |
| QLCDNumber::Bin | 3 | Binary |
If the display is set to hexadecimal, octal or binary, the integer equivalent of the value is displayed.
This type determines the visual appearance of the QLCDNumber widget.
| Constant | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| QLCDNumber::Outline | 0 | gives raised segments filled with the background color. |
| QLCDNumber::Filled | 1 | gives raised segments filled with the windowText color. |
| QLCDNumber::Flat | 2 | gives flat segments filled with the windowText color. |
This property holds the current number of digits displayed.
Corresponds to the current number of digits. If QLCDNumber::smallDecimalPoint is false, the decimal point occupies one digit position.
By default, this property contains a value of 5.
This property was introduced in Qt 4.6.
Access functions:
| int | digitCount () const |
| void | setDigitCount ( int numDigits ) |
See also smallDecimalPoint.
This property holds the displayed value rounded to the nearest integer.
This property corresponds to the nearest integer to the current value displayed by the LCDNumber. This is the value used for hexadecimal, octal and binary modes.
If the displayed value is not a number, the property has a value of 0.
By default, this property contains a value of 0.
Access functions:
| int | intValue () const |
| void | display ( const QString & s ) |
| void | display ( int num ) |
| void | display ( double num ) |
This property holds the current display mode (number base).
Corresponds to the current display mode, which is one of Bin, Oct, Dec (the default) and Hex. Dec mode can display floating point values, the other modes display the integer equivalent.
Access functions:
| Mode | mode () const |
| void | setMode ( Mode ) |
See also smallDecimalPoint(), setHexMode(), setDecMode(), setOctMode(), and setBinMode().
This property is deprecated.
This property holds the current number of digits displayed.
Access functions:
| int | numDigits () const |
| void | setNumDigits ( int nDigits ) |
See also digitCount.
This property holds the style of the LCDNumber.
| Style | Result |
|---|---|
| Outline | Produces raised segments filled with the background color |
| Filled (this is the default). | Produces raised segments filled with the foreground color. |
| Flat | Produces flat segments filled with the foreground color. |
Outline and Filled will additionally use QPalette::light() and QPalette::dark() for shadow effects.
Access functions:
| SegmentStyle | segmentStyle () const |
| void | setSegmentStyle ( SegmentStyle ) |
This property holds the style of the decimal point.
If true the decimal point is drawn between two digit positions. Otherwise it occupies a digit position of its own, i.e. is drawn in a digit position. The default is false.
The inter-digit space is made slightly wider when the decimal point is drawn between the digits.
Access functions:
| bool | smallDecimalPoint () const |
| void | setSmallDecimalPoint ( bool ) |
See also mode.
This property holds the displayed value.
This property corresponds to the current value displayed by the LCDNumber.
If the displayed value is not a number, the property has a value of 0.
By default, this property contains a value of 0.
Access functions:
| double | value () const |
| void | display ( const QString & s ) |
| void | display ( int num ) |
| void | display ( double num ) |
Constructs an LCD number, sets the number of digits to 5, the base to decimal, the decimal point mode to 'small' and the frame style to a raised box. The segmentStyle() is set to Outline.
The parent argument is passed to the QFrame constructor.
See also setDigitCount() and setSmallDecimalPoint().
Constructs an LCD number, sets the number of digits to numDigits, the base to decimal, the decimal point mode to 'small' and the frame style to a raised box. The segmentStyle() is set to Filled.
The parent argument is passed to the QFrame constructor.
See also setDigitCount() and setSmallDecimalPoint().
Destroys the LCD number.
Returns true if num is too big to be displayed in its entirety; otherwise returns false.
See also display(), digitCount(), and smallDecimalPoint().
This is an overloaded function.
Returns true if num is too big to be displayed in its entirety; otherwise returns false.
See also display(), digitCount(), and smallDecimalPoint().
Reimplemented from QObject::event().
This signal is emitted whenever the QLCDNumber is asked to display a too-large number or a too-long string.
It is never emitted by setDigitCount().
Reimplemented from QWidget::paintEvent().
Calls setMode(Bin). Provided for convenience (e.g. for connecting buttons to it).
See also setMode(), setHexMode(), setDecMode(), setOctMode(), and mode().
Calls setMode(Dec). Provided for convenience (e.g. for connecting buttons to it).
See also setMode(), setHexMode(), setOctMode(), setBinMode(), and mode().
Calls setMode(Hex). Provided for convenience (e.g. for connecting buttons to it).
See also setMode(), setDecMode(), setOctMode(), setBinMode(), and mode().
Calls setMode(Oct). Provided for convenience (e.g. for connecting buttons to it).
See also setMode(), setHexMode(), setDecMode(), setBinMode(), and mode().
Reimplemented from QWidget::sizeHint().
© 2008-2011 Nokia Corporation and/or its subsidiaries. Nokia, Qt and their respective logos are trademarks of Nokia Corporation in Finland and/or other countries worldwide.
All other trademarks are property of their respective owners. Privacy Policy
Licensees holding valid Qt Commercial licenses may use this document in accordance with the Qt Commercial License Agreement provided with the Software or, alternatively, in accordance with the terms contained in a written agreement between you and Nokia.
Alternatively, this document may be used under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation.


